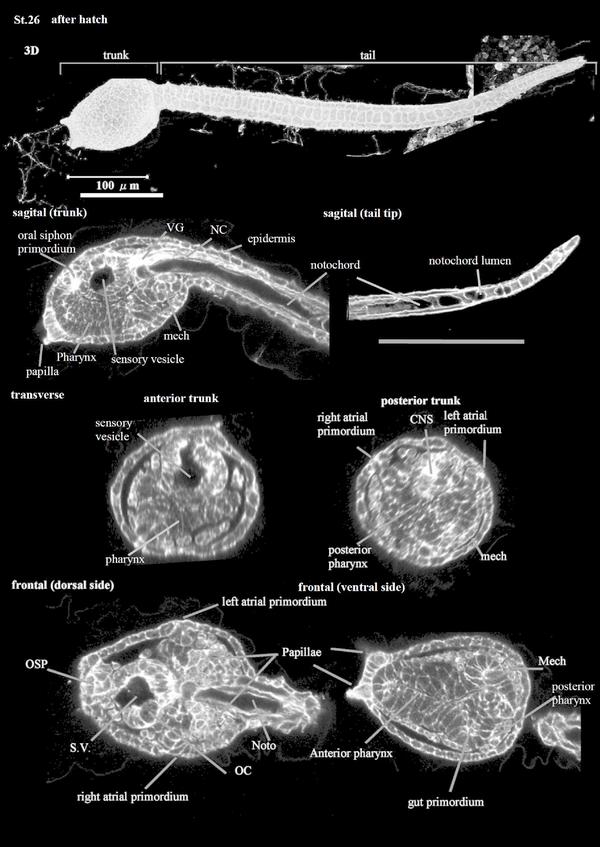
Stage 26
This is the Hatching Larva Stage (CirobuD:0000049; 17.5 h). The larva has a roundish trunk and immature papillae (CirobuA:0000675) with round tips; it exhibits irregular tail (CirobuA:0000797) movements. Eight strips of epidermal cells (CirobuA:0000594) constitute the tail epidermis (CirobuA:0000738). The larval pharynx (CirobuA:0000682) shows a narrow lumen (Hirano and Nishida, 2000). The larval nervous system is subdivided into a central and peripheral nervous system. The former, as described above, contains several entities, for example, the otolith and the ocellus with lens cells (CirobuA:0000648), photoreceptors (CirobuA:0000683), and pigment cup cells (CirobuA:0000685); and the visceral ganglion with its motor neurons. The larval peripheral nervous system (CirobuA:0000681) is differentiating and each epidermal sensory neuron, i.e., the Rostral Tail Epidermal Neurons (CirobuA:0000709), the Dorsal Caudal Epidermal Neurons (CirobuA:0000589), and the Ventral Caudal Epidermal Neurons (CirobuA:0000757), shows dendritic arbors. A vacuolated notochord extends as an elongated structure in the tail. The oral siphon primordium (CirobuA:0000670) is in the form of an epidermal invagination not yet communicating with the pharynx lumen. The atrial siphon primordia (CirobuA:0000368), the pair of invaginations of the dorsal-lateral trunk epidermis, called also atrial placodes (CirobuA:0000908), are not yet open to the exterior. The trunk is covered by a double-layered tunic (CirobuA:0000750) that, at this stage, is not well distinguishable at the histological level: the inner compartment of the tunic (CirobuA:0000882), bordered by the inner cuticular layer (CirobuA:0000883), and the outer compartment of the tunic (CirobuA:0000884), bordered by the outer cuticular layer (CirobuA:0000885).